What the law says
The main provisions related to obtaining a property tax deduction are regulated by the following regulations:
- Article 220 of the Tax Code of Russia - this establishes the possibility of obtaining such a deduction for certain categories of citizens;
- Federal Law No. 212-FZ - determines the procedure for partial refund of funds;
- Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 21, 2008 No. 03-04-05-01/123 regulates the issue of receiving a deduction by the second spouse.
Download for viewing and printing:
Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “Property tax deductions”
Federal Law of July 23, 2013 No. 212-FZ “On Amendments to Article 220 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation”
What is a tax deduction?
This definition means the possibility of a partial return of money spent on the construction or purchase of housing. This right applies only to citizens of the Russian Federation and only after registration of the right to the plot (clauses 1, 2, 6, clause 3, clauses 4, 5 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, the amount of the deduction depends on the actual expenses incurred by the taxpayer, but cannot exceed the norms established at the legislative level.
Who does it apply to?
As mentioned above, only a citizen of the Russian Federation who has incurred monetary expenses for:
- Construction of a country house;
- Acquisition of private home ownership;
- Purchase of living space, including with the use of borrowed funds (mortgage lending).
A prerequisite for a tax deduction is that the recipient must belong to the category of taxpayers, and appropriate deductions are made in respect of him. In particular, here we are talking about paying income tax in the amount of 13%.
Important! Without a taxable base, applying a property deduction becomes technically impossible.
Private households and tax deduction
There are two options here:
- The owner built a residential building. It should be noted here that the right to take advantage of privileges is reserved only for owners of buildings suitable for habitation and registration. For example, if you have built a small country house, which according to its technical characteristics cannot be considered a residential building, the deduction is not provided (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/08/2018 N 03-04-07/7700);
- Completion of construction. A common situation: a person acquires unfinished construction and completes the construction on his own. However, an important nuance must be taken into account here: such real estate must appear in the contract precisely as an object of unfinished construction.
Terms of service
The first thing to remember is that the provision of a tax deduction is allowed only on an application basis. In addition to the application, 4 conditions must be met:
- Russian citizenship;
- The official source of income on which tax is paid;
- Documentary evidence: title documentation for the development site, receipts and receipts;
- The completed house is suitable for registration and housing.
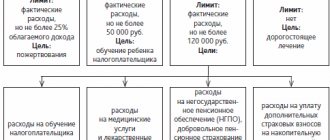
Allowable Costs
This includes the following expense items (clause 3, clause 3, article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Purchase of land for individual housing development;
- Acquisition of an unfinished construction project;
- Ordering design and technical documentation;
- Expenses for construction and finishing materials (In this case, these expenses can be included in the deduction after the state registration of ownership of the house (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 6, 2018 No. 03-04-07/88679), as well as expenses for work and services for house construction;
- Supply and connection of utilities.
What is excluded
It is quite natural that not all construction costs are subject to partial reimbursement. The tax benefit does not apply, for example, to the following expenses:
- Redevelopment or reconstruction of a property, even if this work is approved by the supervisory authorities;
- Construction of additional floors or extensions suitable for habitation;
- Installation of plumbing and gas equipment;
- Construction of outbuildings on a personal plot: sheds, garages, chicken coops, bathhouses, etc.
In general terms, the deduction is only relevant for residential buildings and work necessary to put the building into operation. For example, you can get a tax deduction for connecting water and gas pipes to your home. There is no longer any cost for connecting a shower cabin or gas water heater.
Property deduction when building a house
But you can always contact the local administration with an application to transfer a country house into a residential one, if it meets the necessary conditions, and after re-registration you can apply and receive a deduction for the costs of building this house.
Returning a tax deduction from the construction of a country house has its own characteristics. It is necessary to carefully look at how the property is recorded on the certificate. In accordance with paragraph 6, paragraph 3 and paragraph 2, paragraph 1 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-05/7-652 dated October 29, 2010, part of the amount can only be returned for a residential building, in which registration (registration) is allowed.
When can I use this privilege?
You can contact the territorial division of the Federal Tax Service about this after ownership of the house has been registered.
In particular, a tax deduction becomes possible after the state registration procedure, when the house is entered into the Unified State Register of Real Estate and the homeowner is issued a corresponding certificate. It should be noted that you need to apply for a tax deduction the next year after ownership rights arise. For example, if you built a house and went through the state registration procedure in 2019, you can apply for a property deduction in 2020.
Collecting information
- Certificate of state registration of ownership: extract from the state register;
- Certificate of income filled out in accordance with the established form 2-NDFL;
- Declaration filled out in form 3-NDFL;
- Payment documents certifying expenses incurred: receipts for the purchase of building materials, contracts with contractors, etc.;
- Russian passport;
- Application for tax benefits.
If the construction was carried out using borrowed funds, you will need a copy of the agreement with the financial institution and a certificate certifying the amount of interest paid.
Compensation amount
Strict financial limits apply for tax deductions. In particular, only the tax for individuals is subject to reimbursement. Currently, this is 13% of the amount of earnings or other profits. At the same time, the law sets an upper limit on the amount from which expenses incurred can be reimbursed.
Available maximum
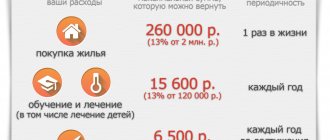
If we turn to the provisions of the Tax Code, the nominal amount of the deduction is determined at 2,000,000 rubles.
We remind you that you can return 13% of the set value. In total, you can count on no more than 260,000 rubles as a tax deduction. If the house was built using borrowed funds, and the mortgage agreement was concluded after January 1, 2014, it is possible to partially reimburse the interest paid on the loan. However, the amount of such expenses is also limited and amounts to 3,000,000. The general principle applies here: only 13% of the maximum amount is subject to reimbursement. As a result, you can receive no more than 390,000 rubles for the interest overpayment.
Important! The tax deduction cannot exceed the amount of tax payments to the state budget. Therefore, such subsidies can be carried forward to the next reporting period. This rule applies until the entire due amount is received by the taxpayer (Article 216, paragraphs 9, 11, Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; paragraphs 1 - 3, Article 2 of the Law of July 23, 2013 No. 212 -FZ).
Income tax refund for the construction of a private house
- agreement for the purchase of a building plot or the purchase and sale of unfinished buildings;
- any invoices, receipts, checks, receipts, bank statements confirming the amount of your expenses;
- acts of acceptance and transfer of work performed by construction companies or employees of public utilities (for construction, installation of communications, finishing, and so on).
In general, a taxpayer is entitled to a refund of 13% of the costs incurred. At the same time, the maximum amount with which personal income tax is reimbursed cannot exceed 2 million rubles. That is, no matter how much it costs the taxpayer to build a new house, the most he can return is 260 thousand Russian rubles. But if the actual cost of housing was less than 2 million, the missing amount can be “raised” next time, during the construction of another housing. Thus, you can build as many houses as you like, but the total amount of personal income tax returned will not exceed 260 thousand.
We recommend reading: In Which Cases Do the Bailiffs Have the Right to Impose an Encumbrance on a Vehicle
Reasoned refusal
The deduction is not provided in the following cases:
- The costs of construction (purchase) were not borne by the applicant: for example, a person was provided with financial assistance for the construction of a house;
- The application is not submitted by the owner of the property;
- The house was built using maternity capital or other types of state funds;
- The purchase and sale agreement was concluded between close relatives;
- The right to receive a property deduction was exercised earlier;
- The cash payout limit has been reached;
- The building is not suitable for living.
In addition, refusal is possible if the documents are filled out incorrectly. However, in this case, it is possible to resubmit the application after eliminating all inaccuracies.
Compensation for construction
When recovering deductions for the construction of a private house, not all funds can be returned. The full list is specified in Article 220 of the Tax Code. The declaration takes into account the following expenses:
- costs of acquiring a land plot for individual housing construction;
- purchase of an unfinished building;
- purchase of construction and finishing materials;
- payment for services of individuals or legal entities;
- money spent on ordering design and estimate documents;
- means for bringing communications into the house (electricity, gas, water, sewerage).
There are a number of expenses for which you will not be able to receive income tax:
- redevelopment of an already built house;
- addition of additional buildings to the finished building, construction of a bathhouse, garage and other utility facilities;
- repair or reconstruction of a finished, registered house;
- installation of plumbing and other equipment.
There are cases when a citizen makes payments for the purchase of a home and at the same time begins repair work on it. This raises two main questions: can he return the money spent on construction materials and finishing work{q} And is it possible to change the previously declared deduction amount{q}
The IRS allows these items to be added to the refund list, even if it has already been compiled. Until notification of receipt has been received, it is allowed to add additional items and change the deduction amount if the amount does not exceed the limit.
We suggest you read: How should you pay for overtime hours if you have time off?
For example: citizen Ivanov built a house on a plot of land and registered it as residential. Expenses amounted to 1.5 million rubles. This year he filed a declaration for a personal income tax refund and received it. But in the same year he carried out repair work for another 500 thousand rubles and after its completion he submits a new declaration for the return of the deduction for repairs. The total declared amount is 2,000,000 rubles, from which he will receive his 13%.
You can get your money back not only for the construction of a house, but also for its repairs for any period.