This question usually arises among homeowners who are planning to build a high fence, but are not sure whether this is allowed by law. There are many reasons for erecting a high fence - from the reluctance to expose your private life to considerations of banal security - but it is better to clarify all the nuances before the start of work, so that later you do not have to quarrel with neighbors or even go to court.
In this article we will explain what heights are allowed for fences for individual housing construction, and which SNiPs are responsible for what.
IZHS is an abbreviation for individual housing construction. The term refers to detached buildings of no more than three floors intended for one family. Individual housing construction includes not only a house, but also garages, sheds, extensions and superstructures, outbuildings located on land owned by the owners.
Norms and rules for developing a land plot for individual housing construction
The law contains a clear definition of the concept of “individual residential building”.
The legislator identified the following main criteria:
- the house should have no more than 3 floors;
- its total area should not be more than 1500 square meters;
- constructed objects should not go beyond the “red line”.
If your plot area is no more than 1200 square meters, you can build only one residential building on it.
In addition to the residential building itself, you can additionally erect such buildings as:
- greenhouse;
- bath, sauna;
- garage;
- other structures intended for economic or other purposes.
Objects constructed on the site must be separated from public areas, which include the surrounding areas and roads. Before starting construction work, a “red line” should be established. As a rule, the area from the road is fenced off. In the process of carrying out construction work, it is necessary to retreat from the “red line” by a certain distance. Thus, the distance from the road should be 5 meters, and if there is a passage there, it should be at least 3 meters.
Thus, the “red line” is a kind of boundary of the territory within which the owner of the site has the right to construct a structure.
If you fail to comply with this requirement and go beyond the “red line,” you may be sued. Please note that the judicial authority has the right to make a decision obliging you, at your own expense, to demolish all structures that extend beyond the established border. The “red line” must be indicated on all plans of the planning project.
It follows that care must be taken in advance to ensure that the conventional boundary, which is not marked in any way on the ground, becomes visible. Before starting construction work, be sure to erect a fence that symbolizes and actually defines this boundary. This way, you will not only have a visual representation of where you can build, but also an obstacle that physically prevents you from violating the requirements of the law.
The legislation provides for rules and established standards governing the installation of a fence:
- there must be a distance of at least 3 meters from the residential building to the fence of the neighboring plot;
- between other buildings and the fence the minimum permissible distance is 1 meter;
- shrubs can be planted 1 meter from the fence of a neighboring property, small trees - 2 meters, and for tall trees a distance of 4 meters is established;
- from the fence of a neighboring plot to buildings such as a bathhouse, sauna or shower, the minimum permissible distance is 8 meters.
The distances given here are legal requirements and must be observed. Violation of these requirements may lead to troubles in the process of interaction with neighbors and may result in you being brought as a defendant in a lawsuit.
To prevent problems that may arise due to planning and construction, observe the following fundamental principles:
- the most important building on the land should be considered a residential building;
- the division of the site for the purpose of carrying out construction work on it must be carried out, taking into account the location of the “red line”;
- buildings should be placed so that they protect the site from winds, but do not lead to excessive shading (in most cases, the best option would be to place them in the north or north-west of the site);
- It is recommended to separate outbuildings from the area directly adjacent to the residential building.
From the above recommendations it follows that the site should be divided into zones, each of which has its own purpose with the corresponding location of objects located on the site.
There are 3 types of such zones:
- for living – a house intended for human habitation should be located here;
- for conducting economic activities - cellar, garage, garden, vegetable garden, sheds, enclosures, cages, pens for animals, etc.;
- for recreation - playgrounds for children, gazebos, swimming pools, etc.
Where can I find a city zoning map?
See land use and development rules here.
How to divide a plot of land, read the link:
The legislative framework
According to paragraph three of Art. 39 of the Federal Law “On Cadastral Activities”, not only tenants and owners of plots, but also those persons who use the land under the right of free or lifetime use can carry out the land surveying procedure within the SNT.
Before carrying out measures to measure boundaries, it is mandatory to notify neighbors along the SNT. This norm is enshrined in paragraph 8 of Art. 39 of Federal Law No. 221 “On Cadastral Activities” dated July 24, 2007.
The procedure for developing a land plot
The main regulatory act regulating the procedure for carrying out construction work is the Town Planning Code. It contains a clear definition of the concept of individual housing construction. The Town Planning Code is considered the main act that determines the procedure for the construction of construction projects. Approved and current standards for the construction of construction projects are available in SNIP. The most significant characteristics established in relation to assigned territories for individual housing construction can be found in SNIP 20-10-99.
Legislative acts fix and consolidate the basic requirements relating to the construction of various structures. In order to competently organize the process of construction work, you should first devote time to drawing up an organizational plan. To do this, you will also need to obtain a plan of your territory.
Next, obtain permission to carry out construction work on your site, and then visit the architectural department located in your administration. Please note that the permit has a limited, although quite long, validity period. It is usually issued for 10 years.
If before the expiration of this period the plot has passed to a new owner, then he may well take advantage of the permit, which will still be in force. This may seem strange at first glance, but the permit is tied to a specific territory and is not nominal.
Rules for placing buildings on a garden plot
Compliance with all the listed norms on the site remains on the conscience of its owner, since by violating them, he can only cause harm to himself and his family. In addition, if the owner wants to officially register his buildings and submits the building itself and documents to the state commission to obtain permission to put it into operation, then if these standards are violated, he will most likely be denied this. True, the current legislation allows not to accept country houses and other buildings into operation, and ownership is registered only on the basis of a declaration, but the availability of such documents can play a decisive role in resolving controversial issues.
We recommend reading: If I Pay a Writ of Execution for a Debt Monthly, Can the Bailiffs Take Action Against Me?
Timeframe for site development
If a plot of land has not been used by its owner for its intended purpose for 3 years, it may be confiscated. A plot of land can still be confiscated from the owner if it has not been used for its intended purposes within three years. But local administrative authorities have the authority to determine a longer period for construction.
However, this time interval does not include the period required for research. In addition, they can exclude the time when the land plot was impossible to use due to natural disasters.
If local authorities raise the issue of confiscating a site, they must first issue the owner a warning about the violations identified.
The plot can be put up for sale through an auction, but only after the owner informs the administrative body of his consent.
What is it and why do you need to divide the land?
Let's figure out why you need to do land surveying in gardening? This is because if there is no document confirming ownership rights, then other papers will not help prove your rights.
In addition, one of the main tasks of the process of surveying public land in SNT is to establish precise boundaries on the sides of the site and subsequently receive a document indicating that the land has an owner. Without this procedure, it is impossible to draw up documents for the privatization of the site.
There are cases when the land is owned by the owner without the above procedure. In this case, it turns out that without land surveying, the land cannot be registered as property, that is, from a legal point of view, it was appropriated by squatting, and this is already a violation.
Attention! Another significant advantage of carrying out land surveying in a gardeners’ association is the opportunity to receive up to 10% of excess territory, if any is available for landscaping.
Situations where a dacha plot has not been used for a long time, and then other objects are put in its place or a new owner appears, unfortunately, often occur. Such unpleasant incidents can be avoided only after complete paperwork.
As a rule, ten percent is taken from those plots whose tenants did not take care of timely registration. In favor of land surveying, we can note the fact that people who did not manage to register the land for gardening needs within the deadline set before January 1, 2020, will no longer be able to do this. Lands left without registration will be considered the property of the state.
Land surveying of a garden plot can be carried out by companies licensed to carry out such activities, or by cadastral engineers. If there is no license, this cannot be recognized as a legal distinction.
Fire safety during land development
SNIP 30-02-97 regulates fire safety rules for a private home.
It sets the following standards:
- the minimum distance between stone houses is set to 6 meters;
- wooden buildings must be at least 15 meters apart from each other;
- if one building is stone and the other is wooden, they must be separated by at least 10 meters.
This applies to houses located on adjacent plots. If your neighbor has an object dangerously close to your home, try asking your neighbor to fix the problem. It is easiest to negotiate if the building is not in use. For your part, you will also make sure that your actions do not violate these norms. At the same time, the distance between buildings on the site is not regulated.
If a garage is adjacent to a residential building, follow these rules:
- the garage must be at least a meter away from the property line;
- there should be a distance of at least 3 meters from your house to the neighboring plot.
If there is an outbuilding near the house, the following standards apply:
- from your residential building to the territory of the neighboring plot, a distance of 1 to 3 meters is established;
- the distance from your outbuilding to the boundaries of the neighboring plot must be at least 4 meters.
Compliance with these requirements will help minimize the occurrence of situations related to the occurrence of fires and their spread, as well as make it easier to combat them both on your property and among your neighbors.
Settlement of buildings and structures from the fence of their site
The set of rules 53.13330.2019 specifies the distance from all buildings to the fence located on a summer cottage, as well as a garden area in SNT. Similar standards for ownership as individual housing construction are specified in SP 30-102-99.
Fence between summer cottages
Outbuildings, outbuildings, engineering structures
The regulations regarding the setback of outbuildings in relation to the fence are scattered throughout all documents. Therefore, for clarity, information for garden plots in SNT and individual housing construction buildings is summarized in the table below.
Requirements for a residential building individual housing construction
The law sets a limit on the height of the house, which should not exceed 3 floors. Its other dimensions are determined by the area of the site and development standards.
But at the same time, the law establishes minimum values for the area of the house and its individual rooms:
- There must be at least one living room or common room, the smallest area of which can be 12 square meters;
- The kitchen area cannot be less than 6 square meters;
- A combined bathroom should have an area of 3 square meters, and a separate bathroom should have 1.8 square meters for the bathroom, and 0.96 for the toilet;
- The hallway must have a minimum area of 1.8 square meters.
The height of the living space is also adjustable. In private houses, its minimum value is 2.5 meters. If there is a second floor or attic, the staircase leading to it should be at least 0.9 meters wide. If the house has an attic with a living room, kitchen or bathroom, it is allowed to reduce their area by 15%.
Building standards in relation to the fence of the neighboring plot
For convenience, the standards for buildings on a summer cottage (garden plot) in relation to the fence of adjacent properties are summarized in a separate table.
| Building, structure, object | Distance to neighbor's fence, meters |
| Residential building | Not less than 3 |
| Detached garage, sauna, bathhouse, gazebo | 1 |
| Chicken coop, sheepfold, other buildings for birds and livestock | 4 |
| Greenhouse | 1 |
| Artificial reservoir such as a pond, swimming pool | 3 |
| Hives | 10 |
| Trees over 3 m high | 3 |
| Trees less than 3 m | 2 |
| Shrub less than 2 m high | 1 |
Standards for engineering and technical support of a residential building
In a private house, first of all, you need to take care of the power supply and installation of technical equipment.
It must contain:
- sewerage;
- ventilation system;
- heating system;
- electricity supply;
- gas supply;
- water supply.
But the reality is that these requirements are rarely fully met.
The law clearly states that if there is no power supply, the house must be declared unfit for permanent residence. But even to this discrepancy, officials often turn a blind eye.
Eliminating these shortcomings is not a big problem if you live in a populated area. But if the house is located outside the settlement or in a sparsely populated rural area, certain difficulties may arise.
In the latter case, take care of purchasing autonomous systems, such as compact wind and solar power plants, an independent waste collection system, and heating devices. Nowadays, prices for these devices have become affordable. Please use qualified personnel to install all this equipment.
If you have the necessary skills to install it yourself, follow the rules below:
- When installing an autonomous sewage system, it is necessary to ensure that the base of the central collector is at least 1 meter above the groundwater level;
- The heating system must produce a power of 10 W per 1 square meter of housing area;
- When connecting electricity, it is necessary to ensure a span height under open lines of 2.75 meters. As for autonomous generators, their installation and operation is carried out in accordance with their operating instructions;
- For an autonomous water supply system, it is necessary to drill a well and ensure filtration of underground water. To be able to use hot water, you can install a personal boiler room, or a boiler room for all surrounding houses by agreement with the neighbors. The use of electric or gas boilers is allowed.
It is strictly prohibited to independently connect the gas supply to your home.
Receipt procedure
The document is prepared by a specialized organization that has the right to carry out land management work, including land surveying. For the preparation of the document by the organization where the ordered services are received, a fee is charged according to the internal tariff.
Read more: When is an examination of land management documentation needed?
To draw up a land surveying plan, submit a corresponding application and pay for the work. The initiator of action can only be a person who has submitted sufficient documents confirming the rights to the object specified in the application or is directly interested in it.
Drawing up a plan requires mandatory boundary work and is carried out in the following sequence:
- Receiving and processing information relating to the land plot.
- Informing interested parties in the upcoming land survey (individuals and legal entities owning adjacent plots).
- Identification and coordination of the size and boundaries of the site.
- Carrying out geodetic work with surveying.
- Compilation and analysis of the obtained data by a cadastral specialist.
- Drawing up a land surveying plan, which is then submitted for verification and registration to the body that controls the cadastral registration process.
- Registration of a cadastral passport. After receiving approval and entering information into a single database, a cadastral extract is prepared that determines the geographical coordinates of the land.
- The boundary plan is recognized as valid if it is certified by the seal and signature of the cadastral engineer.
Be sure to read it! What documents are needed to register guardianship?
The hand-delivered boundary plan includes, as one of the annexes, an act of agreeing on the location of the site with other interested parties. It is attached on the back in the section with graphic information about the site.
Required papers
The main conditions for obtaining a land survey plan are: carrying out the survey procedure and confirming legal rights to this land plot.
The list of documents required for drawing up a boundary plan includes:
- Application from the person who has the rights to the land in question (filled out according to the sample).
- Certificate of registration of ownership.
- A document establishing the right to own land (certificate of inheritance, resolution of a judicial body, other official bodies ordering the allocation of a plot in favor of a specific person, etc.)
- Personal document proving the identity of the applicant. For legal entities, it is necessary to submit constituent documents.
- Technical documentation of the BTI, if a building is being erected on the land.
- Cadastral documents (extract and territory plan).
Often, in the process of determining the boundaries of adjacent plots, disputes arise between neighbors. If it is not possible to agree on boundaries at the stage of surveying and drawing up a plan, the owner goes to court to resolve the dispute.
Timing and cost
Operations with land and registration of documents for it differ in the duration of the process.
Ordering the services of cadastral engineers and drawing up a document based on collected and analyzed information requires certain costs. For this reason, if you intend to make transactions with this property in the future, you must be prepared for certain expenses of time and money. There are no uniform prices for cadastral services due to the impossibility of bringing various individual characteristics under unified rules. However, each region has its own average tariffs applied by local specialized organizations.
The cost of services is affected by:
- Features of the location of the site and its geometry.
- Belonging to a certain category of land.
- The price range that has developed in a specific constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
On average, obtaining land surveying and planning services in the Moscow region will cost from 10 to 30 thousand rubles, and in the suburbs of St. Petersburg the prices are lower - approximately 7-8 thousand rubles. In more remote areas of the country, costs will range from 5 thousand rubles.
The difficulty in determining exact costs is due to the fact that a separate boundary plan is rarely ordered. Usually, its production is accompanied by an order for services for measurements, approval and registration of a cadastral passport.
The process of approval, data collection, taking measurements and analyzing the information received requires a certain amount of time.
The following information will allow you to plan further work on the preparation of land documentation:
- applying for the required paper – 1 day;
- consideration of the application and verification of information received from the customer – 1 day;
- performing land surveying work – 1 day;
- processing of received information and coordination with interested parties - at least 2 days (in complex situations - several weeks);
- in the absence of a common opinion and consent of the owners of adjacent plots, the consideration of disputes is transferred to the court, and the duration of this stage reaches up to several months;
- The final compilation of data and the compilation period in days takes no more than 2x.
Due to the impossibility of taking into account all the features of land surveying, the exact time for production is not regulated by law, and the validity period is limited only by the occurrence of new circumstances in which changes are planned to be made to the characteristics of the object.
Structure: what parts does it consist of?
All types of boundary plans consist of a graphic and text part.
The graphic part reflects:
- site diagram on the ground;
- site boundaries;
- drawing with information about the area and other indicators;
- location of all buildings and geodetic objects.
The text part reflects the following information:
- initial data;
- on the approval of boundaries;
- about neighboring areas;
- conclusion of a cadastral engineer.
FOR REFERENCE! The boundary plan is prepared on paper and electronic media. The electronic form must be protected by a digital signature of the cadastral engineer.
Text part
The text part contains the main information characteristics of the land plot and includes the following data :
- Initial indicators on the basis of which the engineer made calculations;
- Data on what measurements and calculations were made during the process of drawing up the document;
- Data on what areas or parts of areas were formed or what changes were made to them (if any);
- Data on those plots that allow access to this site;
- Conclusion of the specialist who drew up the plan;
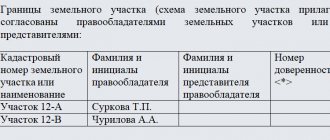
- An approval act signed by all interested parties (owners of adjacent plots).
Conclusion
The conclusion began to be included in the document starting in 2008 as a section of its text part.
Initially, this part of the plan was a special explanation, justification for the work carried out and how the border defining the area of the site runs.
Since 2012, such a part began to be included when necessary and it is drawn up to describe the actions performed.
It is used in situations where the definition of boundaries or any actions in the process of their installation require reference to legislative acts or certain facts to prevent the recognition of boundaries as invalid or illegally established.
Border approval act
Most of the land plots for which the specialist determines the boundaries in the process of drawing up the plan have adjacent plots directly adjacent to it.
In such situations, in order to ensure that the rights of the owners of such plots are not affected, a procedure for their approval becomes necessary.
To do this, a general meeting is held , at which the engineer presents a previously drawn up plan and clearly explains how the boundaries of the site will be drawn.
If there are no contradictions, all interested parties sign a separate document.
If all areas (or some) previously had approvals for passing boundaries, such an act may not be available .
The grafical part
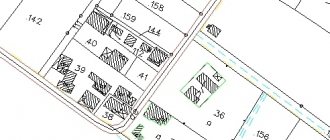
The graphic part of the boundary plan is a direct display of the passing boundaries of the site, defining the boundaries of the property of a person or organization and it contains the following :
- Object diagram;
- Location of the site taking into account the accepted display scales;
- The drawing itself of the site and its parts (if there is a need to highlight the components);
- Outlines of the nodal (turning) points of the allotment, between which there are lines defining the boundaries of the property.
In what formats is it issued?
The plan is presented first on paper . The document is executed in two original copies, one of which is received by the direct customer.
Currently, in parallel, the engineer is also preparing an electronic version , which, if desired, can be separately provided to the customer who has entered into a contract for boundary work.
Legend
The following notations are accepted:
- The boundaries are determined by lines, with those that existed before cadastral work drawn in black, and those that appeared during the land surveying process in red.
- A solid line is used for boundaries whose location is determined with sufficient accuracy, and a dotted line is used with insufficient accuracy. The thickness of the lines is also regulated - 0.2 mm.
The length of the dotted line is 2 mm, the distance between them is 1 mm. Help: The required accuracy of measurements depends on the purpose of the land. For example, for gardening and individual housing construction it is 0.2 meters.
There are 4 options for marking boundaries:
- Already existing, defined with sufficient accuracy - a solid black line.
- Existing, but defined with insufficient accuracy - a dotted black line.
- Newly formed or refined, if the accuracy is sufficient - with a solid red line.
- New, but lacking in accuracy - dotted in red.
The characteristic (turning) point of the border is indicated in black:
- a solid circle with a diameter of 1.5 mm, if its location is established accurately;
- circle of the same diameter if the location is not determined precisely enough.
Land plots and their individual parts are also designated in a strictly defined way. The sections are written like this:
- Those that originally existed, from which others are formed by division, merger or redistribution - with a colon and a number from the cadastral plan. Additionally, they are highlighted by underlining and at the same time italics.
- Plots whose boundaries are being clarified or changed are marked with a colon and the number indicated in the cadastral plan.
- Formed from state or municipal lands, as well as by consolidation or redistribution - a colon, the letters “ZU” and a number.
- Formed using a section or separation from an existing one - a colon, the number of the original section, a colon, the letters “ZU” and a number.
- Multi-circuit section - with the section number and the serial number of the contour in parentheses.
And their parts are like this:
- Already existing ones - colon, number, slash and part number.
- Vanishing - the same, but using italics and underlining.
- When designating the parts being formed, “chzu” and the serial number of the part are added to the number of the land plot after the slash.
- Parts included in the composition during redistribution - the number of the original site with a colon, the letter “p” and the number of the part. If there are several such numbers, the number of the cadastral quarter is added in front (without separators).
- Included in newly formed plots (from municipal or state lands) - with a colon, the letter “p” and a number.
- When designating a part of a multi-circuit section, “chzu” and the part number are added to its number after the slash, and then, in parentheses, the contour number.
Be sure to read it! Deed of gift for a house: sample and how to draw it up in 2020
Turning points are indicated:
- existing before, unchanged or with a specified location in number;
- those that have ceased to exist - with a number written in italics and underlined;
- newly formed ones - with the letter “n” and a number.
Thanks to the use of uniform symbols, not only the surveyor can understand what exactly is shown on the diagram. Anyone who knows these signs is capable of this.
What is a multi-circuit allotment?
A multi-circuit section consists of several parts - closed contours.
It comes in two types:
- consisting of separate parts (two or more);
- a plot of land with inclusions, as if “cut out” from it.
The first type is formed when it is necessary to allocate land, if it is impossible to form a whole plot of the required area. In essence, these are several plots under one cadastral number.
The second type occurs when among the lands from which the plots are allocated there are territories whose transfer to private individuals is impossible. For example, if power line supports are located on them. These “internal” territories form additional contours. Otherwise, the registration and disposal of such lands is carried out as usual, without restrictions.
The concept of “multi-circuit land plot” was introduced on March 1, 2008 with the entry into force of Law No. 221-FZ of July 24, 2007. Before this, the name “single land use” was used.
Both it and the individual parts had their own cadastral numbers. Lands registered this way retain both their numbers and name.
A boundary plan is an important document containing a lot of information about a land plot. It must be properly drawn up both when the site is formed and with any changes to its boundaries.